Learn
What is Liquidity?
Video Transcript
Liquidity is an important concept to understand about financial markets. It is something that impacts not just FX but all asset classes. So, what is liquidity?
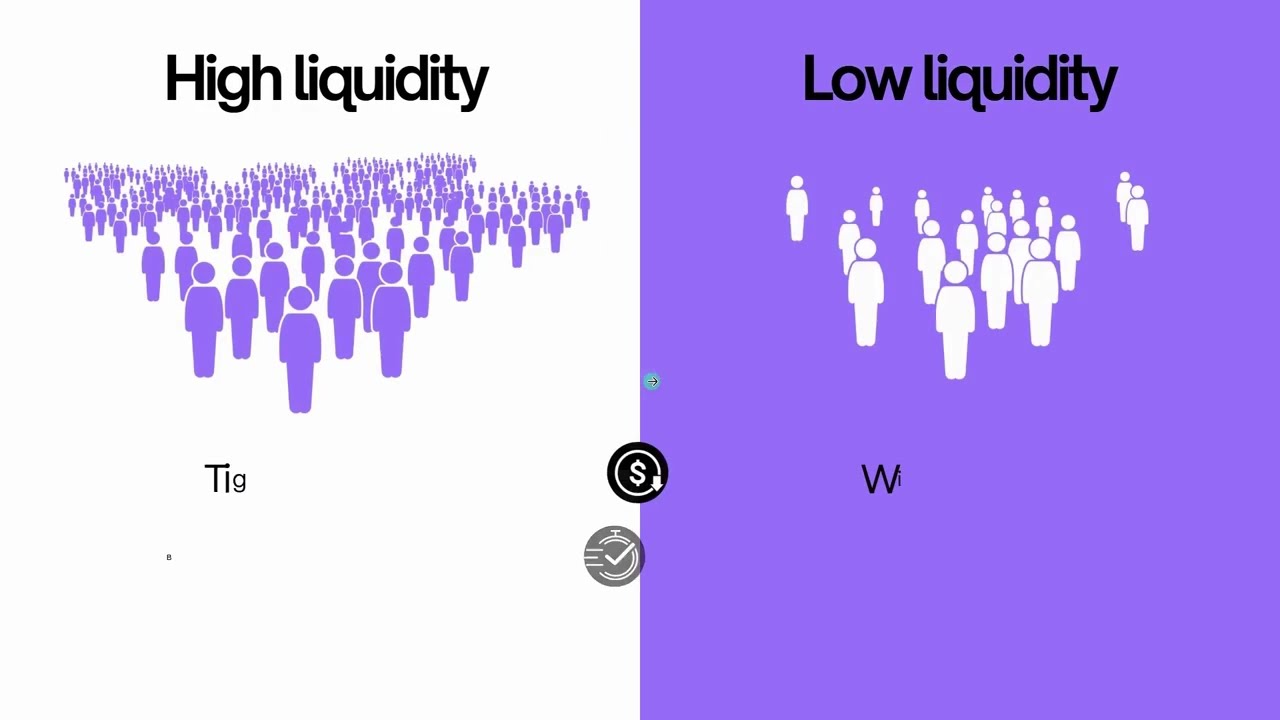
Think of liquidity as the oil in a car’s engine. Just like an engine needs enough oil to function properly, the market needs liquidity. Without enough oil, an engine becomes sluggish, overheats, and can even seize up. Just as oil reduces friction in an engine, liquidity helps reduce friction in financial markets, allowing for efficient price discovery and smoother trade execution. In simple terms, liquidity refers to how easily and quickly you can buy or sell an asset without significantly affecting its price. The more buyers and sellers actively trading an asset, the more liquid it is. We can break it down like this… When there is more liquidity or market participants actively trading an asset, it usually means…
Tighter Spreads—This means the spread, which is the difference between the buying and selling price, is smaller, making it cheaper to enter and exit trades. Spreads are usually wider for low liquidity or illiquid assets, leading to higher trading costs. Now if you are completely new to trading, you might be asking yourself what is the spread? When you look at a price chart, there are two prices you need to be aware of. The top one is called the ask price, that’s the red line on this chart. And the bottom one is called the bid price, that’s the blue line on the chart.
The spread is the difference between the buy price (ask) and the sell price (bid) of an asset. It’s basically the small gap between what the market is willing to buy something for and what it’s willing to sell it for. You can think of the spread as a built-in cost of placing a trade. As soon as you open a trade, you’re down by the amount of the spread, because you bought at a higher price than you could immediately sell at. When you place a buy trade, your buy trade will be opened at the ask price, and will be closed at the bid prices. And when you place a sell trade, your sell trade will be opened at the bid price, and will be closed at the ask prices.
This difference is very important to understand, because the spread will impact where your trades are opened and where your trades are closed. Let’s take a look at this chart as an example. Here we can see that price for the EURNOK currency pair was trading at 11.51. Even though the current price was at 11.51, we can see that the ASK price at that time was trading at 11.52, with a spread of about 11 pips. That means, if you wanted to open a BUY trade when price was at 11.51, due to the spread your BUY trade would have opened at 11.52, to account for the spread. This is not just important to consider when opening trades, but also important when closing trades.
In this example, a trader placed a sell trade on the NOKJPY currency pair. The sell trade was opened at 14.274, with a Stop loss set at 14.311, and a take profit set at 14.200. Notice that even though the price moved past the targeted closing price, this trade was not closed. The reason for that is because a sell trade closes at the ask price(the red line). So, this trade will only be closed at the targeted closing price of 14.200, when the price moves low enough so that the ASK price (the red line), reaches 14.200. In other words, only when the price moved lower and the ASK price reached 14.200, only then the trade was closed at the targeted price. This is very important to understand as the spread can make a huge difference between a losing trade and a winning trade.
So, coming back to liquidity and why it matters, here’s a quick visual of why liquidity matters. This chart is the currency pair USDJPY on the left, and then a chart of Copper on the right. Notice that USDJPY has a 1-pip spread, while Copper has a much wider spread of about 83 Dollars. So, this can make a very big difference in the outcome of trades, which is why so many trader prefer to trade markets that have higher liquidity. The second reason why liquidity matters, is due to trade execution. The higher the liquidity, the better the Trade Execution. With more market participants, orders are more likely to be filled closer to the intended price, reducing the risk of being filled at unfavourable levels. In markets with low liquidity, traders run the risk of bigger slippage, leading to trades executed at worse-than-expected levels.
What do we mean by Slippage?
Slippage occurs when there is a mismatch between the expected price and the actual price at which a trade is executed. This happens because market prices are constantly changing due to supply and demand, and in fast-moving or low-liquidity conditions, price shifts can happen faster than orders can be processed. In highly liquid markets with stable price movement, slippage is usually smaller because there are plenty of buyers and sellers to match orders smoothly. But in volatile or very illiquid markets, prices can jump between order placement and execution quite erratically, leading to a different fill price than expected. This means that when you place an order, your trade might be executed at the next available price, which could be higher, lower, or the same as the price you intended.
Let’s do a quick explanation of how this works. This is a chart of gold. Now imagine for a second you wanted to buy gold, but your are trading at the same time that some very important US economic data is being released. Now imagine you press the buy button just as the US news comes out, and immediately within a few split seconds price gaps higher as market volatility ramps up due to the news event. This awkward gap in price is what we call slippage or price gaps. Because price jumped or gapped higher within a few milliseconds of the news release, it means that your buy order that would have been filled at 3203, will now only be filled or executed at the new available price, which is 3216. This is a good example of why trading products with higher liquidity is preferred by many traders, because it limits the amount of slippage a trader might experience.
The other benefit of higher liquidity is overall Price Stability. High liquidity means prices move more gradually and predictably, whereas illiquid markets can see wild price swings. In other words, lower liquidity leads to more erratic price behaviour or more volatility. These two charts is a great way to visualize this. On the left, we have the EURUSD currency pair on a 5-minute chart, and on the right we have the EURNOK currency pair on the right. Both charts are 5-minute charts, both pairs include the EUR, and both of them is showing price action for the exact same day and session. But look at how different both of these two markets traded. The EURUSD on the left saw gradual price moves throughout the session, with smaller candles and far less volatility. The EURNOK on the right on the other hand, looks like a total mess with huge spikes, no clear direction and just a huge amount of unwanted volatility in price behaviour. This chart is a really good example of why liquidity matters when choosing the symbols or assets you want to trade.
Relevant videos